Tutorial
 Introduction
Introduction
FunEVA was designed to simplify and assist in the selection of functionally relevant Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNP) for large-scale
genotyping studies.
This tool is based on many existing tools to perform functional annotation and pathogenicity prediction of each variant.
 General Features
General Features
Sortable tables
 |
Each table is sortable by clicking on the head cell of a column. You can also sort a table by multiples columns, by clicking and sliding or by hidding and showing columns using
interactive "Customize options" popups. |
 |
| Use the pager to browse the table with the first page, previous page, next page and last page buttons. Choose how many results you want to display. |
|
Popups
This popups can :
- warm you that you have validated a new step during the analysis
- inform you that new informations has been added to result table
Console


Here you can find:
- The action FunEVA needs you to realize to proceed to the next step
- The name of processing analyze
- The analyze advancing percentage
 FunEVA_prot
FunEVA_prot
INPUT
FormatFunEVA_prot accepts TSV input format with three case-sensitive headers needed :
- Gene Symbol
- Var g.
- Var p.
You can also specify other optional headers that allow you for example to sort your data more easily (date, age, gender...).
You can download a file example here.
Upload
Your file can contain up to 3,000 variations. If you have more data to analyze thank you to as many files as you need.
If your file does not contain the headers described above you will be redirected to an error page and your analysis can not be launched.
Pre-computing
After loading your data will be analyzed first to obtain all the information needed to launch modules FunEVA_prot.
This step of pre-computing is divided into three parts :
- Mapping of Gene Symbol to Gene ID
- Mapping of Gene ID to UniprotID
- Parsing of Uniprot XML files
After pre-computing it exists several possibilities :
- No error message :
- Pre-computing step is finished
- Redirection to a form to manually adding some Gene IDs
- You must enter Gene IDs of some Gene Symbol which have not been recognized. This error probably happens because you have entered some Gene Alias instead of Gene Symbols.
- To correct it please complete the form and reload your file.
- An error message in console during Mapping of Gene ID to UniprotID
- This error means that some variations can not be analyzed by FunEVA. This error probably happens when UniprotID doesn't exist for the Gene ID entry.
- To correct it you must delete this variations and upload your file again.
Analyze

- Compare properties of the reference amino acid and the observed amino acid:
- Chain flexibility
- Interaction Modes
- Chain Hbonds
- Weight
- Isoelectric Point
- Hydrophobicity
- Properties
- Results available in detailed report of each SNV
The Grantham score caracterizes the difference of amino acids properties giving a pathogenicity score.
Higher is the score higher is the pathogenicity prediction.
- Grantham class :
- Score between 0 and 50 : Conservative
- Score between 50 and 100 : Moderately conservative
- Score between 100 and 150 : Moderately radical
- Score higher than 150 : Radical
- Results are available in table results and in variation report.
- GERP identifies constrained elements in multiple alignments by quantifying substitution deficits (see this page for more details).
GERP++>2 in human genome, as this threshold is typically regarded as evolutionarily conserved and potentially functional. - PhastCons is a program for identifying evolutionarily conserved elements in a multiple alignment, given a phylogenetic tree. It is based on a statistical model of sequence evolution called a phylogenetic hidden Markov model (phylo-HMM) (see this page for more details)..
- PhyloP score is based on multiple alignments of 46 genomes. The larger the score, the more conserved the site. It is similar to GERP++ but therefore, even conceptually similar tools may sometimes generate drastically different results.
All these score were retrieved from the dbNSFP (LJB2_DB) starting from June 2013.
-
SIFT predicts whether an amino acid substitution affects protein function. SIFT prediction is based on the degree of conservation of amino acid residues in sequence alignments derived from closely related sequences, collected through PSI-BLAST.(see this page for more details).
In previous versions of dbNSFP (ljb_sift), the scores were calculated as 1-SIFT. In the updated version 2 (ljb2_sift), the scores were now the SIFT score itself. This mean a variant with score<0.05 is predicted as deleterious.
- PolyPhen (Polymorphism Phenotyping) is a tool which predicts possible impact of an amino acid substitution on the structure and function of a human protein using straightforward physical and comparative considerations (see this page for more details).
- MutationTaster evaluates disease-causing potential of sequence alterations (see this page for more details).
-
All the informations about domains, motifs and regions are extracted from international reference databases and are then analysed.

Example of SORL1 protein with an impacted domain
- SMART : SMART (a Simple Modular Architecture Research Tool) allows the identification and annotation of genetically mobile domains and the analysis of domain architectures (see this page for more details).
- Prosite : PROSITE is a protein database. It consists of entries describing the protein families, domains and functional sites as well as amino acid patterns and profiles in them (see this page for more details).
- Pfam : Pfam is a large collection of protein families, represented by multiple sequence alignments and hidden Markov models (HMMs) (see this page for more details).
- Interpro : InterPro provides functional analysis of proteins by classifying them into families and predicting domains and important sites (see this page for more details)
- Stability effect: Mupro allows assessment of the impact of the amino acid substitution on the protein's stability.
-
The keywords INCREASE or DECREASE mean respectively an increase of the stability or a decrease of the stability.
(Example :
 )
)
-
The keywords INCREASE or DECREASE mean respectively an increase of the stability or a decrease of the stability.
(Example :
- Protein structure modeling: the Protein Model Portal
-
Protein Model Portal will try to find an experimental structure of the submitted protein.

- You will be able to view several templates of 3D proteiin structure ordered by sequence identity.
- An analysis of amino acids is given showing their several properties with a colored scheme.
-
Protein Model Portal will try to find an experimental structure of the submitted protein.
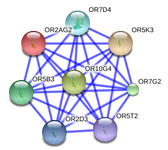
- Protein interaction
- The drawing of functional protein association networks is done using String database.
- You will find for every submitted variation known and predicted protein-Protein interactions.
- Ontologies and pathways
- Ontologies (GO terms) allow to understand the protein functions (F), general process (P) in which the protein is involved and its localisation (C).
- The pathways are a list of terms which refers to general functions of the protein linked to major processes of the organism.
- Mutations repositories links
-
A set of cross-links are available from the analysis to :
- OMIM (Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man)
- COSMIC (Catalogue Of Somatic Mutations In Cancer)
- Ensembl Variation (Ensembl)
- dbSNP annotations (NCBI - dbSNP)